Table of Contents
Blockchains are brilliant at many things. But knowing whether it’s raining in Rio or if ETH just hit $3,000? Not one of them.
To understand oracles, picture this: A blockchain is like a vault – ultra-secure, airtight, and sealed from the outside world.
Oracles? They’re the keyhole. The microphone. The translator. They’re how blockchains hear, see, and react to real-world events. Without oracles, smart contracts can’t fetch price feeds, settle prediction markets, or trigger insurance payouts based on actual weather.
In this guide, we’re pulling back the curtain on oracles – how they work, why they matter, and where this invisible but essential infrastructure is heading.
What Are Oracles?
Think of oracles like the 'plug-ins' for blockchains. They bring outside info-like crypto
prices, sports scores, or weather data–into the sealed, self-contained world of smart contracts.
Say a smart contract is programmed to say: "Liquidate this loan if Bitcoin crashes below $30K." Cool. But how would it "know" the price? Spoiler: it wouldn't-unless an oracle told it.
Oracles act as the bridge between the blockchain and the real world. No oracles, no useful smart contracts. Just fancy code with no clue what's going on outside.
Oracles are external services that feed off-chain data into a blockchain. In simple terms: they help smart contracts know what's happening in the real world.
A smart contract might say: "If Bitcoin's price drops below $30,000, liquidate this loan." That only happens when a verified BTC/USD price is delivered on-chain by an oracle.
That's where a blockchain oracle comes in - delivering signed, aggregated off-chain data to the chain so contracts can act on it.
Why Blockchains Need Oracles
Blockchains are like those genius math kids in school-unbelievably smart, but completely oblivious to what's going on around them.
They're great at verifying internal transactions and balances, but can't peek outside the chain. They don't browse, don't Google, don't know the score of the Super Bowl-or the ETH price on Coinbase.
That's a problem for DeFi apps that need external truth. Blockchains are deterministic by design. This means they only know what's already on- chain - account balances, smart contract logic, internal transactions.
They don't "browse the web." They don't call an API. They can't check the weather or fetch stock prices.
Yet most DeFi applications rely on external truth:
- A lending protocol needs current asset prices.
- A decentralized insurance app needs weather or event data.
- A prediction market needs to know the winner of an election.
Enter oracles: the on-chain world's ears and eyes. Without oracles, smart contracts are blind. They’re brilliant calculators sealed inside a vault – and oracles are the peepholes.
How Oracles Work (Without Going Full Nerd)
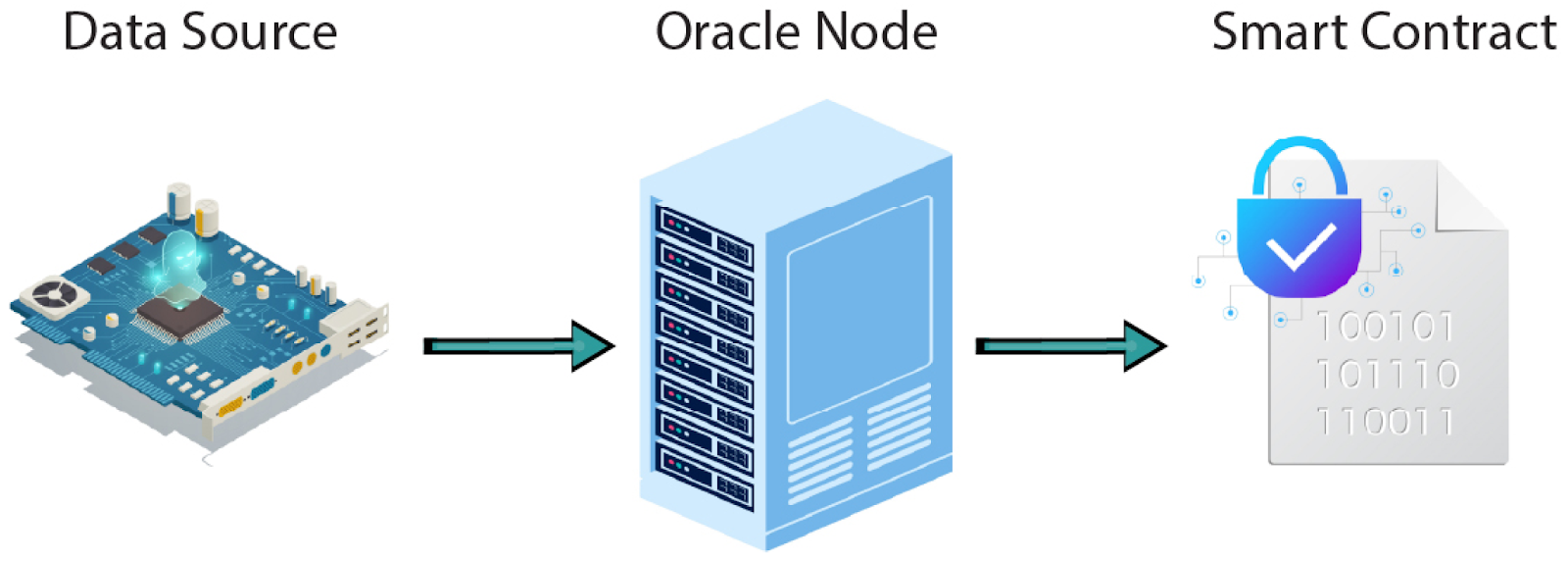
At a high level, the flow looks like this:
1. Data Source
This is where the original data lives – e.g., a crypto exchange (for price data), NOAA (for weather), or a sports API (for match results).
2. Oracle Node / Oracle Network
This is the middleman (or middle-network) that grabs the data, checks it, and passes it to the blockchain.
3. Smart Contract
The brain waiting for input. Once it gets the info, it does its thing – releases funds, executes logic, settles bets, you name it.
Oracles can vary in form:
Centralized Oracles
Run by one party. Fast and simple, but you’re basically putting all your trust in a single server not screwing up or going rogue.
Decentralized Oracles
Pull data from multiple places, compare it, and reach consensus. More robust, but trickier to build and maintain.
Push vs. Pull
Some oracles shove data on-chain regularly (push). Others wait for smart contracts to request it (pull).
Software vs. Hardware
Software oracles deal in APIs and online data. Hardware oracles deal in the physical world – like RFID tags on shipping containers or temperature sensors in vaccine storage.
Leading Oracle Providers (and What Makes Them Different)
The oracle ecosystem has grown rapidly, but a few players dominate the conversation:
1. Chainlink
The OG of decentralized oracles. Chainlink created a decentralized network of nodes that pull data from multiple sources, aggregate it, and deliver it securely on-chain.
- Powers most major DeFi protocols.
- Uses data aggregators to prevent manipulation.
- Offers services like Proof of Reserve, Verifiable Randomness, and Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP).
- Introduced staking to boost security and incentivize honest behavior.
2. Band Protocol

A faster, more scalable oracle solution built on Cosmos. Focused on low-latency data and cross-chain interoperability.
- Often used by gaming and real-time apps.
- Lower gas costs vs Chainlink on certain networks.
3. API3

Takes a novel approach with first-party oracles. Instead of relying on middlemen, API providers run their own oracle nodes, improving data authenticity.
- Advocates for “oracle transparency.”
- Uses Airnode – a plug-and-play oracle node.
4. Pyth Network
Specializes in high-frequency financial data. Targets the needs of institutions, DEXs, and high-volume traders.
- Strong presence on Solana.
- Partners with exchanges like Binance and OKX.
Real Use Cases of Blockchain Oracles
Oracles aren’t some abstract dev tool – they’re powering real DeFi use cases daily:
Price Feeds for DeFi
This is the big one. Lending platforms, synthetic assets, stablecoins – they all rely on accurate price data. Aave, Compound, and Synthetix use oracles to assess collateral, calculate liquidations, and issue assets.
One wrong price feed and… boom – liquidations, exploits, chaos.
Prediction Markets
Projects like Polymarket or Augur need to know who won the election or how many touchdowns were scored. Oracles report the result, which leads to smart contracts paying out accordingly.
Insurance
Take Arbol, for example. It uses weather oracles to automate payouts.
Farm didn’t get enough rain? Smart contract checks the rainfall data and sends your money – no claims adjuster needed.
Supply Chain & Logistics
Oracles paired with IoT sensors track products in real time:
- Verify if goods are kept at a required temperature.
- Confirm if a shipment reached its destination.
Gaming & Randomness
Fair loot boxes and NFTs need randomness so you can’t cheat. Chainlink’s VRF (Verifiable Random Function) gives provably fair outcomes for games and NFT drops.
Beyond Finance: Oracles Powering New Frontiers
While most people associate oracles with DeFi, their real power lies in enabling any decentralized application to interact with reality. And that means their reach goes far beyond finance.
AI + Oracles = Smarter dApps
As AI-generated content and decision-making grows, dApps increasingly need context. Oracles can feed machine learning models with off-chain data, letting dApps personalize services or automate decisions based on real-world variables.
Imagine a decentralized content platform that tailors recommendations based on news sentiment. Or a DAO that shifts its governance rules depending on global regulatory changes. With oracles, that kind of dynamic logic becomes possible.
Healthcare & Bio Oracles
In a world of wearable tech, medical sensors, and decentralized health records, oracles could feed verified health data into insurance, clinical trials, or wellness programs.
- A step tracker oracle could verify exercise in fitness-to-earn models.
- A glucose monitor oracle might enable tokenized health incentives.
Of course, privacy is key here – so zero-knowledge oracles and privacy-preserving computation will be vital.
Environmental Oracles
DeFi isn’t just financial – it’s foundational. Oracles can help track environmental data like air quality, water usage, or carbon emissions.
Projects tokenizing carbon credits or funding climate solutions increasingly rely on proof of impact. Oracles make that provable.
For example:
- A DAO might disburse funding based on oracle-verified deforestation reduction.
- An RWA-backed bond could tie interest rates to real-time pollution data.
The Oracle Problem (And Why It’s Tricky)
The “Oracle Problem” refers to this core contradiction: Blockchains are trustless, but oracles often aren't.
If your DeFi protocol is secure but relies on a single oracle to deliver price data… Well, your protocol isn’t actually secure. You’re just moving the trust issue off-chain.
This creates attack vectors:
- A centralized oracle lies or gets hacked? Funds are drained.
- A flash loan manipulates a price feed? Loans are wrongly liquidated.
- An unreliable node reports bad data? Smart contracts misfire.
Solving this means building trust-minimized oracle networks – decentralized, transparent, and tamper-resistant.
Challenges & Risks of Oracles
Even the best oracle networks face tough problems:
Manipulation Attacks
History is full of examples – and some are costly.
In 2020, bZx, a DeFi lending platform, was hit by multiple flash loan attacks due to oracle manipulation. Attackers exploited price discrepancies by manipulating a low-liquidity asset’s price feed, netting over $1 million in stolen funds.
Similarly, Mango Markets, a Solana-based trading platform, suffered a $100+ million exploit in 2022 when an attacker manipulated the price of MNGO tokens on a low-volume DEX. The manipulated oracle data let them borrow far more than their actual collateral.
Latency & Liveness
An oracle that’s too slow is almost as bad as one that’s wrong.
- Delayed price updates = missed liquidations or easy arbitrage
- Too frequent updates = high gas costs and inefficiency
Balancing speed and reliability is tricky.
Centralization
The 2020 Value DeFi exploit is a classic case. The protocol used the Curve 3pool as a price oracle. An attacker manipulated the pool using a flash loan, skewing the price and draining over $6 million. The problem? They relied on a single data source.
Even in decentralized ecosystems, if your oracle relies on one input, you’re still playing with fire.
Data Accuracy
Decentralization doesn’t fix everything. If multiple oracles all pull from bad sources, you still get junk data. And DeFi doesn’t do “oops.”
Where Oracles Are Headed: The Future
Oracles are turning from simple data bridges into programmable, trustless data layers. Some big trends to watch:
Zero-Knowledge Oracles
Use cryptographic proofs to verify data without revealing sensitive details – perfect for health data, compliance, and privacy-preserving apps.
Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs)
Hardware like Intel SGX allows for secure data processing off-chain, with proofs sent on-chain – bridging privacy and transparency.
Cross-Chain Oracles
Hardware like Intel SGX allows for secure data processing off-chain, with proofs sent on-chain – bridging privacy and transparency.
Real-World Assets (RWAs)
As more real estate, commodities, and bonds get tokenized, oracles will verify their real-world status – making sure that tokenized house or carbon credit actually exists.
How to Get Involved with Oracles
You don’t have to be a cryptographer to interact with oracle systems. Here’s where to start:
- Build with Oracle Data - Chainlink, Band, and others offer APIs and SDKs to plug price feeds into smart contracts.
- Stake in Oracle Networks - Some oracles offer staking – you can secure the network, earn rewards, and vote on governance.
- Monitor Oracle Feeds - Sites like data.chain.link offer dashboards to track oracle performance, data updates, and historical feeds.
- Join Communities - Oracle projects often run hackathons, bounties, and forums. Explore their Discords, GitHubs, and Twitter feeds to stay in the loop.
Conclusion: The Plumbing Behind the Protocols
Oracles don’t get the glory. No “oracle season.” No moon boys on Twitter. But without them? The entire DeFi stack collapses.
They’re the invisible glue. The whisperers. The API wrappers that make smart contracts – well, smart.
So next time a DAO votes, a protocol liquidates, or your NFT game rolls a perfect 69 – thank the oracle.
They’re the bridge between bytes and reality. And in Web3, that bridge is everything.
Disclaimer: The content provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be considered financial or investment advice. Interacting with blockchain, crypto assets, and Web3 applications involves risks, including the potential loss of funds. Venga encourages readers to conduct thorough research and understand the risks before engaging with any crypto assets or blockchain technologies. For more details, please refer to our terms of service.
