Table of Contents
Call it odd, but there’s something powerful about whipping out a wallet and reaching for cash. As paper money sits cozy in a purse, cryptocurrencies sit in a digital wallet. Well, technically, crypto wallets don't store your coins. Instead, they secure your keys (public or private) which unlock access to your tokens on the blockchain.
Wallets for cryptocurrencies can be custodial or non-custodial. Read this article to learn about both types of wallets.
What is a Custodial Wallet?
The private keys of this wallet are held and managed by a third party. This third party is usually a crypto exchange that takes the role of keeping your money safe. Think of it like a safe deposit box at a bank.
Here, you keep your valuable items (cryptocurrencies) in the box. However, the bank holds the key to the box and controls access. While the items are stored, you can perform different actions, meaning that you can deposit or withdraw, but you don't have direct control over the box.
The box, in terms of a custodial wallet, is a mobile or web app. The app comes with a wallet account, and you need to log in to access your funds and perform transactions. The custodial wallet provider is to have strong measures to ensure the security of your assets. An example is the use of two-factor authentication.
What is a Non-custodial Wallet?
These are usually referred to as self-custody wallets. Why? Because you are fully responsible for managing your funds. Think of it like a safe in your own home. You have complete control of your crypto holdings and private keys.
There are several forms of non-custodial wallets. The popular ones are browser-based, mobile, and hardware wallets. A browser-based wallet is a browser extension. The mobile wallet is a downloadable app, and the hardware wallet is a physical device that can be managed offline.
Non-custodial wallets are secured with a seed phrase, a sequence of randomly generated words that stores and generates private and public keys. Think of the phrase as a password. With it, you gain total control of the tokens in your wallet.
Custodial Wallet vs Non-custodial Wallet
Both types of wallets have different features going for them. Read on as we compare the custodial and non-custodial wallets.
Custodian of Private Key
Simply put, a private key is an alphanumeric code a crypto wallet generates, which is then used to authorize transactions.
For a custodial wallet, a third-party service manages the private key. On the other hand, you have complete control and responsibility over a non-custodial wallet.
Security
Custodial wallet services use two storage methods: Hot and Cold. The hot wallet is designed as software (requires internet access). The cold wallet, on the other hand, is a hardware device (no internet access). Both storage methods are secured by a password, making the security level average.
The security for non-custodial wallets is regarded as very strong. This is because only the holder knows the wallet details, reducing the risk of a hack. The only time there can be a breach is if you share the information with someone else.
Backup and Recovery
Custodial wallets are managed by the service provider, who handles backup and recovery. So, even if you lose access to the account, the provider can help you regain it. In the case of a hack, the provider may cover the loss. Most of these exchanges utilize cold storage for safekeeping backup funds.
Backup and recovery is an area in which non-custodial wallets are at a disadvantage. Since the key is kept in your care, any breach would lead to a loss of the stored tokens. While misplacing the hardware wallet would lead to a forfeiture. It's advisable to back up your seed phrase or keep the wallet in a safe location.
Transactions
Non-custodial wallets offer real-time transaction reflection on the blockchain. Transactions are immediately visible and verifiable. This is possible because these wallets operate without intermediaries, allowing for direct interaction with the blockchain.
Custodial wallet transactions take place on a crypto exchange. These exchanges depend on centralization, which can sometimes delay the transaction process.
Examples of Custodial and Non-custodial Wallets
The table below expresses five examples of popular custodial and non-custodial wallets. We would also state the reason for their popularity;
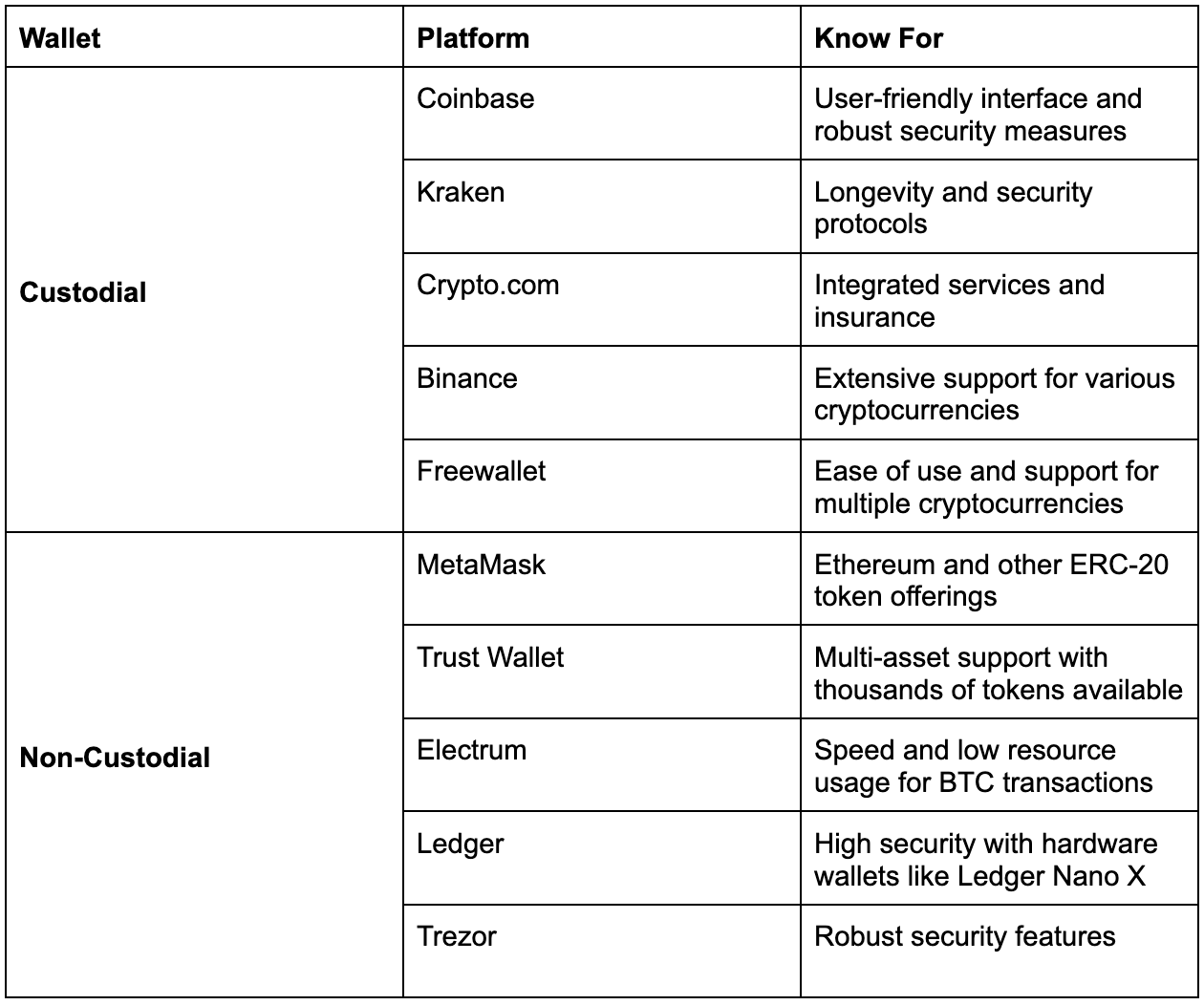
We must state that some platforms offer both custodial and non-custodial wallets. A prime example is Blockchain.com. Offering both wallets allows users to be flexible in managing their crypto assets.
Conclusion: Which wallet to choose?
Choosing a wallet to keep your assets is dependent on your investment strategy and asset management needs. Merging those with the information provided in this article should make it easier to choose wisely. If you seek ease and recovery options, then choose a custodial wallet. However, opt for a non-custodial wallet if you desire complete control over your private keys.
Key Takeaways
- A custodial wallet is one in which a third party manages your private keys. Examples are Venga, Binance, and Kraken.
- A non-custodial wallet is one where you are responsible for keeping your private keys. Examples are MetaMask and Trust Wallet.
- Certain platforms allow users to have either type of wallet. These platforms are known as hybrid crypto exchanges. An example is Blockchain.com.
- Custodial wallets like Venga are popular among people who prefer convenience over control. Meanwhile, users who prioritize full control over convenience prefer non-custodial wallets.
- With a custodial wallet, an investor can recover access if lost because a third party controls the private keys. Access is permanently lost in a non-custodial wallet without the private keys or recovery phrase.
- Choosing between custodial and non-custodial wallets depends on what the user needs. If full responsibility is a priority, a non-custodial wallet is recommended.
Disclaimer: The content provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be considered financial or investment advice. Interacting with blockchain, crypto assets, and Web3 applications involves risks, including the potential loss of funds. Venga encourages readers to conduct thorough research and understand the risks before engaging with any crypto assets or blockchain technologies. For more details, please refer to our terms of service.
